EC2
Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) EC2 is the product name of the virtual machine IaaS Instance Reservation By default, all instances requested are On-Demand, however if instances are reserved for a period of time then there can be significant discounts in consumption.
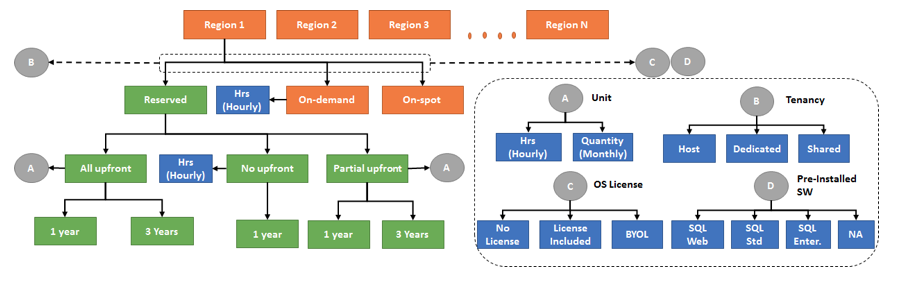
RESERVED – Reserved instances is where your organization would commit to usage for a given time period (i.e. 1-3 years). Discounts can be significant depending on commitment type.
ON-DEMAND – On-Demand instances is where your organization would have no commitment, can start or stop at any time, and pay a simple hourly rate.
SPOT – Similar to On-demand, however your organization will have to “bid” for instances in the AWS market place. Your organization’s instances will keep on running until you stop the instance or the current spot price exceeds your organization’s bid price.
Elastic Block Storage (EBS)
EBS is the product name of the classic block storage service attached to EC2 instances, which traditional operating systems can lay a file system and use. EC2 instances utilize shared bandwidth network and storage operations. For dedicated bandwidth for storage I/O, select an EC2 that is EBS-Optimized.
EBS Snapshots
EBS snapshots are a point-in- time compact copy of data in an EBS volume, which can be access instantaneously, shared, or copied across regions
EC2 Regions
|
Region Code |
Region Names |
| us-east-1 | US East (N. Virginia) (5 AZs) |
| us-west-2 | US West (Oregon) (3 AZs) |
| us-west-1 | US West (N. California) (3 AZs) |
| eu-west-1 | EU (Ireland) (3 Azs) |
| eu-central-1 | EU (Frankfurt) (2 AZs) |
| ap-southeast-1 | Asia Pacific (Singapore) (2 AZs) |
| ap-northeast-1 | Asia Pacific (Tokyo) (3 AZs) |
| ap-southeast-2 | Asia Pacific (Sydney) (3 AZs) |
| ap-northeast-2 | Asia Pacific (Seoul) (2 AZs) |
| ap-south-1 | Asia Pacific (Mumbai) (2 AZs) |
| sa-east-1 | South America (São Paulo) (3 AZs) |
| us-gov-west-1 | AWS GOVCLOUD (2 AZs) |
EC2 Different pricing categories
Current and Previous generation Instance Types
| Instance Family | Current Generation Instance Types | Previous Generation Instance Types |
| General purpose | t2.nano | t2.micro | t2.small | t2.medium | t2.large | m4.large |m4.xlarge | m4.2xlarge | m4.4xlarge | m4.10xlarge | m3.medium |m3.large | m3.xlarge | m3.2xlarge | m1.small | m1.medium | m1.large | m1.xlarge |
| Compute optimized | c4.large | c4.xlarge | c4.2xlarge | c4.4xlarge | c4.8xlarge |c3.large | c3.xlarge | c3.2xlarge | c3.4xlarge | c3.8xlarge | c1.medium | c1.xlarge | cc2.8xlarge |
| Memory optimized | r3.large | r3.xlarge | r3.2xlarge | r3.4xlarge | r3.8xlarge |x1.32xlarge | m2.xlarge | m2.2xlarge | m2.4xlarge | cr1.8xlarge |
| Storage optimized | i2.xlarge | i2.2xlarge | i2.4xlarge | i2.8xlarge | d2.xlarge |d2.2xlarge | d2.4xlarge | d2.8xlarge | hi1.4xlarge | hs1.8xlarge |
| GPU instances | g2.2xlarge | g2.8xlarge | cg1.4xlarge |
| Micro instances | t1.micro |
Hardware Specifications
| Instance Family | Hardware Specification |
| General purpose (T2) |
High Frequency Intel Xeon Processors with Turbo up to 3.3GHz Burstable CPU, governed by CPU Credits, and consistent baseline performance |
| General purpose (M4) |
2.4 GHz Intel Xeon® E5-2676 v3 (Haswell) processors EBS-optimized by default at no additional cost Support for Enhanced Networking |
| General purpose (M3) |
High Frequency Intel Xeon E5-2670 v2 (Ivy Bridge) Processors* SSD-based instance storage for fast I/O performance |
| Compute optimized (C4) |
High frequency Intel Xeon E5-2666 v3 (Haswell) processors optimized specifically for EC2 EBS-optimized by default and at no additional cost Ability to control processor C-state and P-state configuration on the c4.8xlarge instance type |
| Compute optimized (C3) |
High Frequency Intel Xeon E5-2680 v2 (Ivy Bridge) Processors Support for Enhanced Networking Support for clustering |
| Memory optimized (X1) |
High Frequency Intel Xeon E7-8880 v3 (Haswell) Processors Lowest price per GiB of RAM 1,952 GiB of DDR4-based instance memory SSD Storage and EBS-optimized by default and at no additional cost |
| Memory optimized (R3) |
High Frequency Intel Xeon E5-2670 v2 (Ivy Bridge) Processors SSD Storage |
| Storage optimized (I2) |
High Frequency Intel Xeon E5-2670 v2 (Ivy Bridge) Processors SSD Storage & Support for TRIM |
| Storage optimized (D2) |
High-frequency Intel Xeon E5-2676v3 (Haswell) processors HDD storage Consistent high performance at launch time High disk throughput |
| GPU instances |
High Frequency Intel Xeon E5-2670 (Sandy Bridge) Processors High-performance NVIDIA GPUs, each with 1,536 CUDA cores and 4GB of video memory Each GPU features an on-board hardware video encoder designed to support up to eight real-time HD video streams (720p@30fps) or up to four real-time full HD video streams (1080p@30fps) |
GENERAL PURPOSE – General purpose is a hybrid storage offering that utilizes traditional HDDs backed by SSD for performance. All new EBS storage provisioned with EC2 are general purpose by default.
PIOPS – PIOPS is a pure SSD offering where your organization can pay for specific IOPS levels and latency.
MAGNETIC – Magnetic is the legacy EBS offering that is comprised of traditional HDDs only, hence the name “magnetic”. Use of Magnetic EBS volumes should be discouraged.
Instance Store
An instance store provides temporary block-level storage for your instance. This storage is located on disks that are physically attached to the host computer. Instance store is ideal for temporary storage of information that changes frequently, such as buffers, caches, scratch data, and other temporary content, or for data that is replicated across a fleet of instances, such as a load-balanced pool of web servers. While an instance store is dedicated to a particular instance, the disk subsystem is shared among instances on a host computer.
You can specify instance store volumes for an instance only when you launch it. The data in an instance store persists only during the lifetime of its associated instance. If an instance reboots (intentionally or unintentionally), data in the instance store persists. However, data in the instance store is lost under the following circumstances:
- The underlying disk drive fails
- The instance stops
- The instance terminates
Therefore, do not rely on instance store for valuable, long-term data. Instead, you can build a degree of redundancy (for example, RAID 1/5/6), or use a file system (for example, HDFS and MapR-FS) that supports redundancy and fault tolerance. You can also back up data periodically to more durable data storage solutions such as Amazon S3 or Amazon EBS.
Some instance types use solid state drives (SSD) to deliver very high random I/O performance. This is a good option when you need storage with very low latency, but you don’t need the data to persist when the instance terminates or you can take advantage of fault-tolerant architectures.
EBS backed store
You can attach an EBS volumes to one of your instances that is in the same Availability Zone as the volume.
EBS backed instances can be set so that they cannot be (accidentally) terminated through the API.
EBS backed instances can be stopped when you’re not using them and resumed when you need them again (like pausing a Virtual PC). EBS backed instances don’t lose their instance storage when they crash (not a requirement for all users, but makes recovery much faster)
You can dynamically resize EBS instance storage. You can transfer the EBS instance storage to a brand new instance (useful if the hardware at Amazon you were running on gets flaky or dies, which does happen from time to time)
It is faster to launch an EBS backed instance because the image does not have to be fetched from S3.
EBS-Optimized Instances
For an additional, low, hourly fee, customers can launch selected Amazon EC2 instances types as EBS-optimized instances. For C4, M4, and D2 instances, this feature is enabled by default at no additional cost. EBS-optimized instances enable EC2 instances to fully use the IOPS provisioned on an EBS volume. EBS-optimized instances deliver dedicated throughput between Amazon EC2 and Amazon EBS, with options between 500 and 4,000 Megabits per second (Mbps) depending on the instance type used.
Enhanced Networking
Enhanced Networking enables you to get significantly higher packet per second (PPS) performance, lower network jitter and lower latencies. This feature uses a new network virtualization stack that provides higher I/O performance and lower CPU utilization compared to traditional implementations. In order to take advantage of Enhanced Networking, you should launch an HVM AMI in VPC, and install the appropriate driver. Enhanced Networking is currently supported in R3, C3, C4, M4, D2, and I2 instances.
Instance Types:
| Instance Type | vCPU | Memory (GiB) | Instance Storage (GB) | Networking Performance | Physical Processor | Clock Speed (GHz) | Intel AVX | Intel AVX2 | Intel Turbo | EBS OPT |
Enhanced Networking |
| t2.nano | 1 | 0.5 | EBS Only | Low | Intel Xeon family | up to 3.3 | Yes | – | Yes | – | – |
| t2.micro | 1 | 1 | EBS Only | Low to Moderate | Intel Xeon family | Up to 3.3 | Yes | – | Yes | – | – |
| t2.small | 1 | 2 | EBS Only | Low to Moderate | Intel Xeon family | Up to 3.3 | Yes | – | Yes | – | – |
| t2.medium | 2 | 4 | EBS Only | Low to Moderate | Intel Xeon family | Up to 3.3 | Yes | – | Yes | – | – |
| t2.large | 2 | 8 | EBS Only | Low to Moderate | Intel Xeon family | Up to 3.0 | Yes | – | Yes | – | – |
| m4.large | 2 | 8 | EBS Only | Moderate | Intel Xeon E5-2676 v3 | 2.4 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| m4.xlarge | 4 | 16 | EBS Only | High | Intel Xeon E5-2676 v3 | 2.4 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| m4.2xlarge | 8 | 32 | EBS Only | High | Intel Xeon E5-2676 v3 | 2.4 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| m4.4xlarge | 16 | 64 | EBS Only | High | Intel Xeon E5-2676 v3 | 2.4 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| m4.10xlarge | 40 | 160 | EBS Only | 10 Gigabit | Intel Xeon E5-2676 v3 | 2.4 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| m3.medium | 1 | 3.75 | 1 x 4 SSD | Moderate | Intel Xeon E5-2670 v2* | 2.5 | Yes | – | Yes | – | – |
| m3.large | 2 | 7.5 | 1 x 32 SSD | Moderate | Intel Xeon E5-2670 v2* | 2.5 | Yes | – | Yes | – | – |
| m3.xlarge | 4 | 15 | 2 x 40 SSD | High | Intel Xeon E5-2670 v2* | 2.5 | Yes | – | Yes | Yes | – |
| m3.2xlarge | 8 | 30 | 2 x 80 SSD | High | Intel Xeon E5-2670 v2* | 2.5 | Yes | – | Yes | Yes | – |
| c4.large | 2 | 3.75 | EBS Only | Moderate | Intel Xeon E5-2666 v3 | 2.9 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| c4.xlarge | 4 | 7.5 | EBS Only | High | Intel Xeon E5-2666 v3 | 2.9 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| c4.2xlarge | 8 | 15 | EBS Only | High | Intel Xeon E5-2666 v3 | 2.9 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| c4.4xlarge | 16 | 30 | EBS Only | High | Intel Xeon E5-2666 v3 | 2.9 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| c4.8xlarge | 36 | 60 | EBS Only | 10 Gigabit | Intel Xeon E5-2666 v3 | 2.9 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| c3.large | 2 | 3.75 | 2 x 16 SSD | Moderate | Intel Xeon E5-2680 v2 | 2.8 | Yes | – | Yes | – | Yes |
| c3.xlarge | 4 | 7.5 | 2 x 40 SSD | Moderate | Intel Xeon E5-2680 v2 | 2.8 | Yes | – | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| c3.2xlarge | 8 | 15 | 2 x 80 SSD | High | Intel Xeon E5-2680 v2 | 2.8 | Yes | – | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| c3.4xlarge | 16 | 30 | 2 x 160 SSD | High | Intel Xeon E5-2680 v2 | 2.8 | Yes | – | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| c3.8xlarge | 32 | 60 | 2 x 320 SSD | 10 Gigabit | Intel Xeon E5-2680 v2 | 2.8 | Yes | – | Yes | – | Yes |
| g2.2xlarge | 8 | 15 | 1 x 60 SSD | High | Intel Xeon E5-2670 | 2.6 | Yes | – | Yes | Yes | – |
| g2.8xlarge | 32 | 60 | 2 x 120 SSD | 10 Gigabit | Intel Xeon E5-2670 | 2.6 | Yes | – | Yes | – | – |
| x1.32xlarge | 128 | 1,952 | 2 x 1,920 SSD | 20 Gigabit | Intel Xeon E7-8880 v3 | 2.3 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| r3.large | 2 | 15.25 | 1 x 32 SSD | Moderate | Intel Xeon E5-2670 v2 | 2.5 | Yes | – | Yes | – | Yes |
| r3.xlarge | 4 | 30.5 | 1 x 80 SSD | Moderate | Intel Xeon E5-2670 v2 | 2.5 | Yes | – | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| r3.2xlarge | 8 | 61 | 1 x 160 SSD | High | Intel Xeon E5-2670 v2 | 2.5 | Yes | – | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| r3.4xlarge | 16 | 122 | 1 x 320 SSD | High | Intel Xeon E5-2670 v2 | 2.5 | Yes | – | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| r3.8xlarge | 32 | 244 | 2 x 320 SSD | 10 Gigabit | Intel Xeon E5-2670 v2 | 2.5 | Yes | – | Yes | – | Yes |
| i2.xlarge | 4 | 30.5 | 1 x 800 SSD | Moderate | Intel Xeon E5-2670 v2 | 2.5 | Yes | – | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| i2.2xlarge | 8 | 61 | 2 x 800 SSD | High | Intel Xeon E5-2670 v2 | 2.5 | Yes | – | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| i2.4xlarge | 16 | 122 | 4 x 800 SSD | High | Intel Xeon E5-2670 v2 | 2.5 | Yes | – | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| i2.8xlarge | 32 | 244 | 8 x 800 SSD | 10 Gigabit | Intel Xeon E5-2670 v2 | 2.5 | Yes | – | Yes | – | Yes |
| d2.xlarge | 4 | 30.5 | 3 x 2000 | Moderate | Intel Xeon E5-2676 v3 | 2.4 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| d2.2xlarge | 8 | 61 | 6 x 2000 | High | Intel Xeon E5-2676 v3 | 2.4 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| d2.4xlarge | 16 | 122 | 12 x 2000 | High | Intel Xeon E5-2676 v3 | 2.4 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| d2.8xlarge | 36 | 244 | 24 x 2000 | 10 Gigabit | Intel Xeon E5-2676 v3 | 2.4 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
EBS Volume Types
| Solid State Drives (SSD) | Hard Disk Drives (HDD) | |||
| Volume Type | EBS Provisioned IOPS SSD (io1) | EBS General Purpose SSD (gp2)* | Throughput Optimized HDD (st1) | Cold HDD (sc1) |
| Short Description | Highest performance SSD volume designed for latency-sensitive transactional workloads | General Purpose SSD volume that balances price performance for a wide variety of transactional workloads | Low cost HDD volume designed for frequently accessed, throughput intensive workloads | Lowest cost HDD volume designed for less frequently accessed workloads |
| Volume Size | 4 GB – 16 TB | 1 GB – 16 TB | 500 GB – 16 TB | 500 GB – 16 TB |
| Max IOPS**/Volume | 20,000 | 10,000 | 500 | 250 |
| Max Throughput/Volume | 320 MB/s | 160 MB/s | 500 MB/s | 250 MB/s |
| Max IOPS/Instance | 48,000 | 48,000 | 48,000 | 48,000 |
| Max Throughput/Instance | 800 MB/s | 800 MB/s | 800 MB/s | 800 MB/s |
| Dominant Performance Attribute | IOPS | IOPS | MB/s | MB/s |
Authors